Comparison of Circular and Rectangular Wire Harness Connectors
In modern electronic systems and industrial equipment, the selection of wire harness connectors directly impacts system reliability and performance. As two fundamental structural configurations, circular and rectangular connectors each possess distinct advantages and application scenarios. This article provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of these two connector types from multiple dimensions including mechanical characteristics, electrical performance, and environmental adaptability, offering valuable references for engineering design and product selection.
Table of contents
I. Circular Connectors
Circular wire harness connectors are widely used in industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications due to their symmetrical design and excellent sealing performance.

1. Mechanical Properties
- Rotation Resistance: The circular design evenly distributes torsional forces, making it ideal for rotating equipment connections.
- High Protection Rating: IP67/IP68 protection can be achieved through O-rings and threaded lockin
- Blind Mating Compatibility: 360° insertion without orientation, enabling quick installation.
2. Electrical Characteristics
| Characteristic | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Shielding Effectiveness | Omnidirectional EMI shielding, suitable for sensitive signal transmission |
| Current Carrying Capacity | Large-diameter contacts support high-current applications |

3. Typical Applications
- Industrial Automation: M12 sensor connectors
- Automotive Electronics: Waterproof connections in engine compartments
- Medical Equipment: Sterilizable medical interfaces
4. Limitations
- Low Space Efficiency: Symmetrical design occupies more PCB area
- Higher Cost: Precision machining increases manufacturing costs
▷ This design demonstrates exceptional reliability in harsh environments but requires careful consideration in space-constrained applications.
II. Rectangular Connectors
Rectangular connectors have become the mainstream choice in modern electronic devices due to their compact structure and high-density layout advantages.
1. Structural Features
- Space Optimization: Right-angle design maximizes PCB space utilization
- Polarization Design: Asymmetric structure prevents misconnection
- Modular Expansion: Supports combination of multiple signal types

2. Electrical Performance
| Characteristic | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Signal Density | Supports high-density pin arrangement |
| Transmission Rate | Optimized design for high-speed signals |
| Heat Dissipation | Planar contact facilitates heat conduction |
3. Typical Application Fields
- Consumer Electronics: Standard interfaces like USB, HDMI
- Data Centers: High-speed backplane connectors
- Industrial Control: Modular I/O interfaces
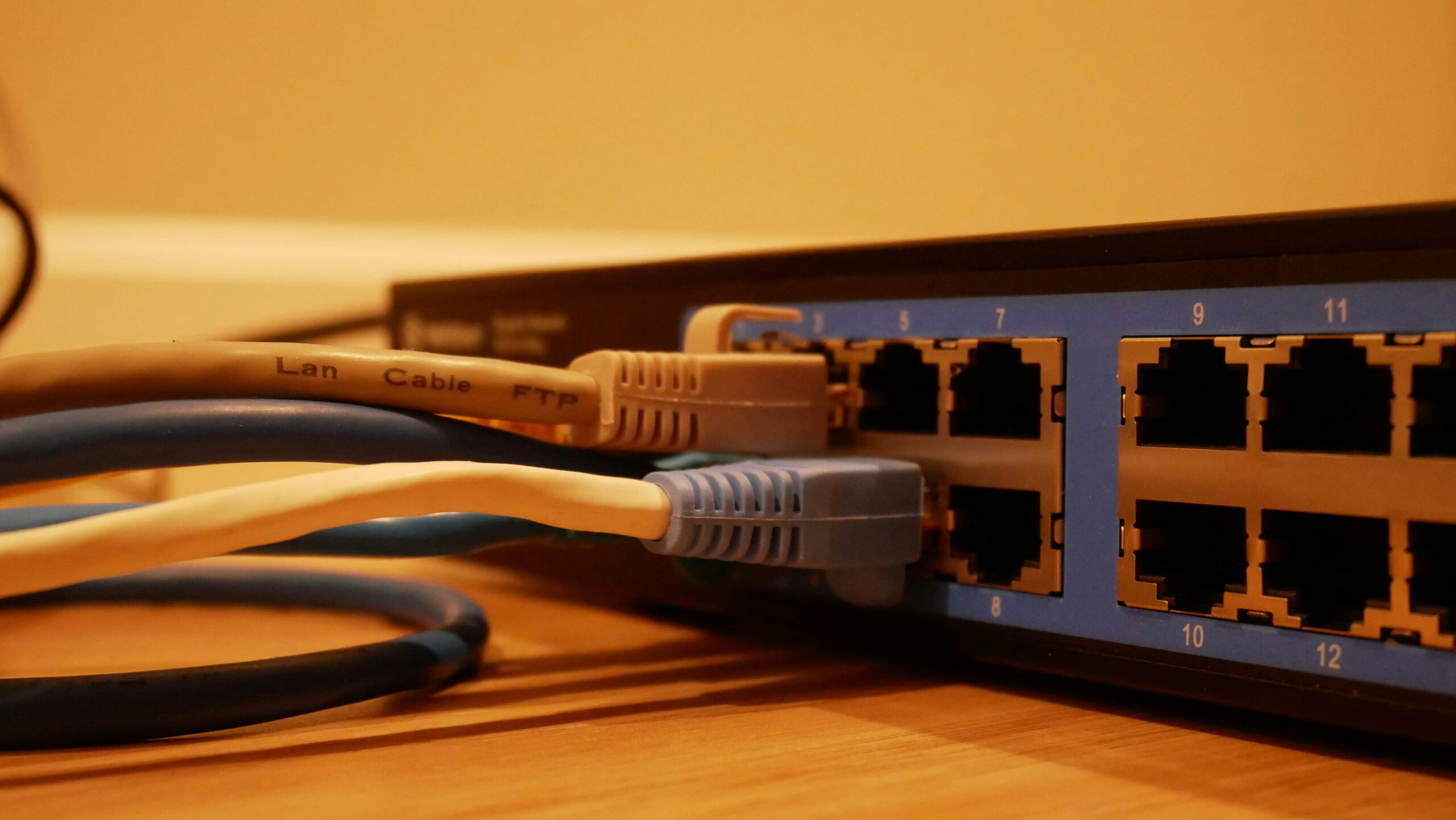

4. Technical Challenges
- Sealing Limitations: Difficult to seal at edges
- Mechanical Strength: Long-term mating may cause structural fatigue
- High-Frequency Interference: Requires additional shielding

▷ Modern rectangular connectors continue to break through traditional limitations through innovative designs and are widely used in 5G and AI equipment.
III. Key Reliability Comparison Points
In practical applications, circular and rectangular connectors demonstrate significant differences in reliability performance, mainly in the following aspects:
1. Mechanical Reliability Comparison
| Comparison Item | Circular Connector | Rectangular Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Vibration Resistance | Threaded locking provides excellent vibration resistance | Clip-on structure prone to loosening under vibration |
| Mating Cycles | Metal housing can exceed 5000 cycles | Typically 1000-3000 mating cycles |
| Structural Strength | Monolithic design offers strong impact resistance | Corners prone to stress concentration |

2. Environmental Adaptability Comparison
- Sealing Performance:
- Circular connector: Naturally suitable for sealing design, easy to achieve IP68 protection
- Rectangular connector: Difficult edge sealing requires special treatment
- Temperature Range:
- Circular connector: -55℃~125℃(metal housing)
- Rectangular connector: -20℃~85℃(standard plastic housing)
3. Electrical Performance Comparison
- EMC Performance:
- Circular connector: 360° omnidirectional shielding, suitable for sensitive circuits
- Rectangular connector: Requires additional shielding measures, prone to edge radiation at high frequency
- Current Carrying:
- Circular connector: Large diameter contacts support high current
- Rectangular connector: Multiple pins in parallel can increase current capacity
4. Maintenance and Cost Comparison
| Factor | Circular Connector | Rectangular Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Installation Difficulty | Requires tools for tightening | Usually supports hand operation |
| Maintenance Cost | Seals require periodic replacement | Clip structure easy to replace |
| Unit Price | Higher(precision machining) | Lower(mass production) |

▷ Conclusion: Circular connectors offer better reliability in harsh environments, while rectangular connectors have cost advantages in conventional applications.
IV. Selection Guidelines
In practical engineering applications, the selection between circular and rectangular connectors requires comprehensive consideration of application scenarios, environmental conditions, and cost factors.
1. Priority Selection by Application
| Application Scenario | Recommended Type | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial automation equipment | Circular connector | Vibration resistance, waterproof/dustproof |
| Consumer electronics | Rectangular connector | Space utilization, cost |
| Automotive electronics | Circular connector | High temperature resistance, corrosion resistance |
| Data center equipment | Rectangular connector | High-speed signal transmission |

2. Environmental Condition Matching
- Harsh environments (high humidity, dusty, corrosive):
- Prioritize circular metal connectors (IP68 rating)
- Normal indoor environments:
- Rectangular plastic connectors offer better cost-performance
- High-frequency vibration scenarios:
- Must use circular connectors with threaded locking
3. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
- Circular connectors: Higher initial cost (+30%~50%)
- Lower lifecycle cost (longer maintenance intervals)
- Rectangular connectors: Lower initial cost
- May require more frequent replacement
4. Special Requirements Consideration
- EMC-sensitive applications: Choose circular connectors with metal shielding
- High-density wiring: Prioritize rectangular board-to-board connectors
- Quick mating requirements: Rectangular snap-fit connectors offer easier operation

▷ Final selection advice: First clarify the key requirements of the application scenario, then balance performance and cost factors.
V. Innovation Trends
With technological advancements, both circular and rectangular connectors are evolving towards intelligent and high-performance solutions.
1. Circular Connector Innovations
| Innovation Technology | Application Advantage | Typical Example |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated smart sensing | Real-time connection monitoring | TE Connectivity’s DEUTSCH Smart Connector |
| Lightweight design | Over 30% weight reduction | Aerospace-grade composite connectors |
| High-speed transmission optimization | Supports 10Gbps+ data transfer | 5G base station specialized circular RF connectors |

2. Rectangular Connector Innovations
- Ultra-high speed transmission:
- Supports PCIe 6.0 standard (64GT/s)
- Modular design:
- Hybrid solutions combining power+signal+fiber
- Self-cleaning technology:
- Nano-coating for dust and corrosion resistance

3. Common Technological Breakthroughs
- Material innovations:
- High-temperature resistant engineering plastics (continuous operating temperature 150℃+)
- Application of recyclable eco-friendly materials
- Manufacturing processes:
- 3D printed micro connectors
- Automated assembly and inspection systems
4. Future Market Predictions
| Application Field | 2025 Growth Rate | Dominant Connector Type |
|---|---|---|
| New energy vehicles | 25% | Circular high-voltage connectors |
| Industrial IoT | 18% | Rectangular modular connectors |
| Medical equipment | 12% | Circular medical-grade connectors |


Leave a Comment