Comparison of Multi-core VS Single-core Cable Applications
In the fields of electrical engineering and electronic devices, the choice between multi-core and single-core cables significantly impacts system performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
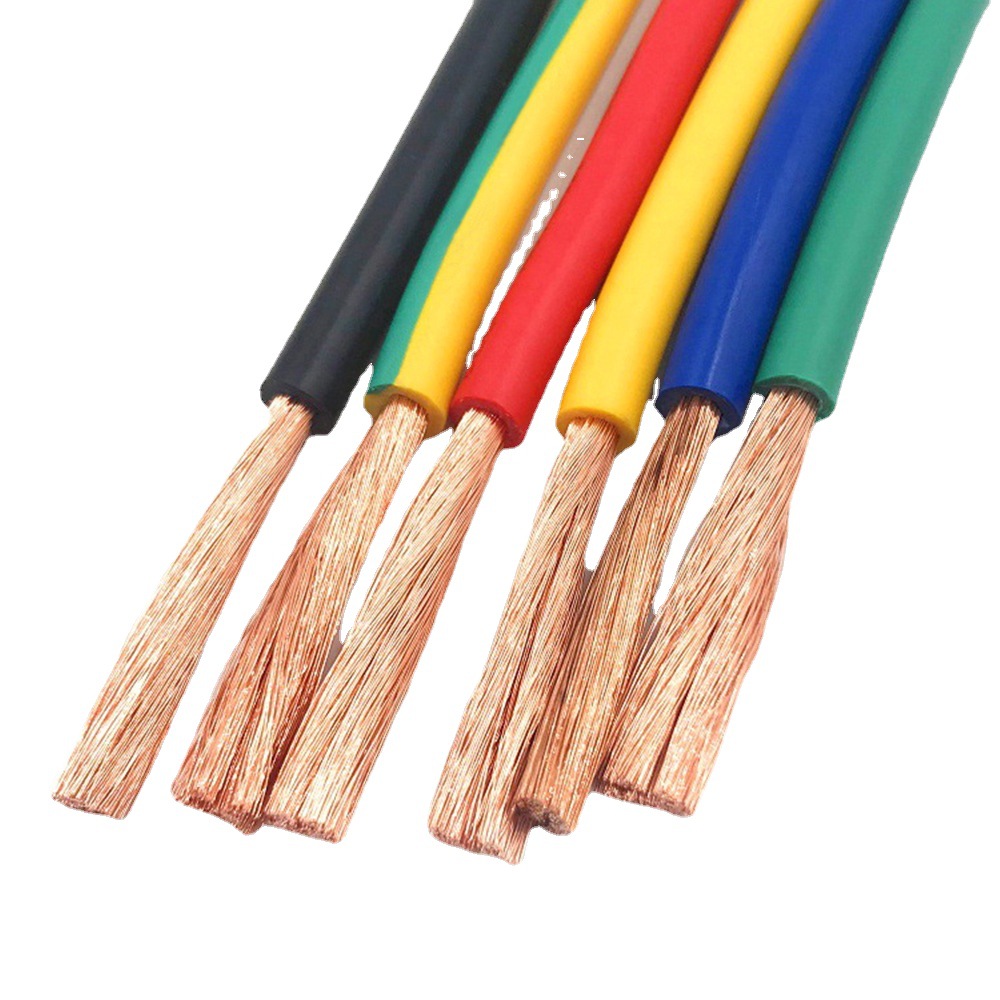
Multi-core cables, composed of multiple stranded thin conductors, offer superior flexibility and noise immunity, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent movement or complex wiring.
On the other hand, single-core cables with their solid thick conductor structure provide higher current capacity and mechanical strength, better suited for fixed installations and high-power transmission.

Table of contents
▶ Comparison of Application Scenarios
Multi-core and single-core cables each have advantages in electrical engineering, electronic devices, power transmission and other fields. Their selection mainly depends on current carrying capacity, mechanical strength, installation environment and flexibility. Below is the main comparison between the two:
| Comparison Item | Multi-core Cable (Stranded Wire) | Single-core Cable (Solid Wire) |
| Conductor Structure | Composed of multiple thin wires twisted together with outer insulation layer | Consists of a single thick conductor with outer insulation layer |
| Flexibility | High (suitable for frequent bending and mobile scenarios) | Low (suitable for fixed installation, prone to damage when bent) |
| Fatigue Resistance | Excellent (withstands repeated bending without breaking) | Poor (bending may damage conductor or insulation) |
| Current Capacity | Relatively low (less affected by skin effect, suitable for small/medium currents) | Relatively high (large conductor cross-section, good heat dissipation, suitable for high currents) |
| Installation Convenience | Flexible routing, suitable for complex wiring | Requires attention to bending radius, suitable for straight or fixed-path installation |
| Interference Resistance | Good (twisted structure reduces electromagnetic interference) | Average (single conductor susceptible to high-frequency interference, requires additional shielding) |
| Typical Applications | Power cords for mobile devices, data cables, control signal wires, headphone cables, etc. | Building power distribution, high-voltage transmission, bus ducts, PV DC cables, etc. |
| Cost | Higher (more complex manufacturing process) | Lower (simple structure, material saving) |
| Suitable Frequency | Suitable for high-frequency signals (less skin effect) | Suitable for low-frequency high current (e.g. 50/60Hz power frequency) |
Key Selection Factors
▪Requires frequent movement? → Choose multi-core cable (e.g. robotic cables, drag chain cables).
▪Requires high current capacity? → Choose single-core cable (e.g. power distribution trunk lines, PV cables).
▪Requires interference resistance? → Choose shielded multi-core cable (e.g. RS485 communication cables).
▪Confined installation space? → Multi-core cables are easier to route (e.g. automotive wiring harnesses).
※ This comparison table can serve as a selection reference. Practical applications require comprehensive evaluation based on specific requirements (such as current, voltage, mechanical strength, etc.).
▶ Application Scenarios of Multi-core Cables
Multi-core cables consist of multiple fine conductors twisted together, with an outer insulation layer or sheath. The feature good flexibility, bending fatigue resistance, and flexible routing, making them widely used in scenarios requiring frequent movement, signal transmission, or complex wiring. Below are the main application areas and specific examples of multi-core cables:
▷ Mobile Devices and Flexible Connections
The high flexibility of multi-core cables makes them an ideal choice for mobile devices, portable appliances, and mechanical moving parts.
• Typical Applications
▪Power cords for household appliances: Rice cookers, vacuum cleaners, electric fans, and other appliances that require frequent movement.
▪Connection cables for electronic devices: USB cables, Type-C cables, HDMI cables, etc.
▪Flexible cables for industrial machinery: Robot joint cables, CNC equipment drag chain cables (resistant to repeated bending).
▪Stage lighting and audio equipment: Moving cables for lighting stands, microphone cables (require pull resistance).
※ Advantages: Bend-resistant, fatigue-resistant, and not prone to breakage with long-term use.
▷ Control and Signal Transmission
Multi-core cables are widely used in low-voltage control, communication, and sensor systems, especially in scenarios requiring anti-interference.
• Typical Applications
▪Industrial automation control cables: PLC signal cables, servo motor encoder cables.
▪Sensor connection cables: Thermocouple wires, pressure sensor wires (multi-core shielded cables reduce interference).
▪Communication cables: RS485 bus cables, CAN bus cables, Ethernet cables (twisted-pair structure reduces crosstalk).
▪Audio cables: Microphone cables, speaker cables (multi-core + shielding layer ensures sound quality).
※ Advantages: The twisted structure reduces electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for high-frequency signal transmission.
▷ Temporary Power Supply and Portable Scenarios
Multi-core cables are easy to retract and move, making them suitable for temporary power supply or outdoor operations.
• Typical Applications
▪Extension cord sockets: Household power strips, mobile distribution boxes for industrial use.
▪Temporary power cables for construction: Construction sites, temporary power supply for exhibitions.
▪Vehicle power cables: Car charging cables, RV external cables.
※ Advantages: Soft and easy to store, adaptable to different environmental layouts.

▷ Medical and Precision Instruments
Medical equipment and laboratory instruments require high flexibility and signal stability from cables.
• Typical Applications
▪Connection cables for medical equipment: ECG machine cables, ultrasound equipment cables.
▪Laboratory instrument cables: Oscilloscope probe cables, precision measurement instrument connection cables.

▷ Special Environment Applications
Certain harsh environments (such as high/low temperatures, oil, or corrosive conditions) require special multi-core cables.
• Typical Applications
▪High-temperature-resistant cables: Industrial furnaces, automobile engine compartments (silicone or Teflon insulation).
▪Oil- and corrosion-resistant cables: Petrochemical equipment, marine engineering cables.
▪Explosion-proof cables: Coal mines, chemical explosion-proof areas (armored multi-core cables).

Summary: Core Advantages of Multi-core Cables
✅ Excellent flexibility → Suitable for mobile and bending scenarios
✅ Strong anti-interference → Ideal for signal transmission
✅ Flexible routing → Suitable for complex wiring
✅ Fatigue resistance → Not easily damaged by long-term bending
○ Multi-core cables are usually the better choice in scenarios requiring frequent movement, stable signals, or limited space.
▶ Application Scenarios of Multi-core Cables
Single-core cables consist of a single solid conductor, featuring simple structure, high current-carrying capacity, and excellent mechanical strength. They are primarily used in fixed installations, high-current transmission, and long-distance power distribution. Below are the main application areas and specific examples of single-core cables:
▷ Fixed Power Distribution Systems
Due to their high current-carrying capacity and stability, single-core cables are widely used in building and industrial power distribution systems.
• Typical Applications
▪Building power distribution mains: BV wires (concealed wiring for home decoration), BVR wires (slightly flexible for exposed wiring)
▪Industrial power distribution lines: YJV cables (cross-linked polyethylene insulation for factory power distribution)
▪Switchgear internal connections: Copper busbars, solid wires (stable high-current transmission)
※ Advantages: Large cross-sectional area, good heat dissipation, suitable for long-term high-load operation.

▷ High-voltage Transmission and Power Systems
Single-core cables perform exceptionally well in high-voltage and long-distance power transmission, especially for overhead lines and underground cables.
• Typical Applications
▪High-voltage overhead lines: ACSR (aluminum conductor steel reinforced, for transmission above 10kV)
▪Substation connection cables: Single-core power cables (e.g., armored YJV62 cables)
▪PV DC side cables: PV1-F solar cables (UV-resistant and anti-aging)
※ Advantages: High mechanical strength, excellent weather resistance, suitable for long-term outdoor exposure.
▷ Underground and Conduit Installation
Single-core cables are suitable for direct burial or conduit installation, especially in environments requiring corrosion and moisture resistance.
• Typical Applications
▪Underground cable trench installation: VV22 armored cables (rodent-proof and pressure-resistant)
▪Pre-embedded conduit wiring: BV wires (embedded in building walls)
▪Subway/tunnel power supply: Flame-retardant cables (e.g., WDZ-YJY low-smoke zero-halogen type)
※ Advantages: Corrosion-resistant outer sheath, suitable for concealed engineering.
▷ High-current Equipment Power Supply
With their large cross-sectional area, single-core cables can carry higher currents and are commonly used for high-power equipment connections.
• Typical Applications
▪Industrial motor power supply: Dedicated cables for heavy machinery and compressors
▪Welding machine cables: Large cross-section single-core cables (e.g., above 35mm²)
▪Data center busways: Copper busbars or large-size single-core cables
※ Advantages: Low impedance, low heat generation, ensuring stable high-current transmission.
▷ Special Environment Applications
Certain harsh working conditions (e.g., high temperature, chemical corrosion) require special single-core cables.
• Typical Applications
▪High-temperature environments: Silicone rubber cables (heat-resistant above 200°C)
▪Chemical corrosion resistance: Fluoroplastic-insulated cables (acid and alkali resistant)
▪Mining cables: Flame-retardant armored single-core cables (e.g., MYPTJ mining cables)

Summary: Core Advantages of Multi-core Cables
✅ High current-carrying capacity → Suitable for high-current transmission
✅ Excellent ✅ Excellent mechanical strength → Tensile and pressure resistant, suitable for fixed installations
✅ Good stability → Not prone to aging during long-term operation
✅ Lower cost → Simple structure with high material utilization
○ Single-core cables are generally a more economical and reliable choice for scenarios requiring high current capacity, fixed installation, or harsh environment use.

▶ Key Selection Factors
In practical engineering applications, the selection between multi-core and single-core cables requires comprehensive consideration of multiple key factors. The following are six core elements that need to be evaluated during selection:
▷ Current Carrying Requirements
• High current scenarios (≥50A):
▪Prioritize single-core cables (large cross-sectional area, good heat dissipation)
▪Typical applications: Power distribution trunk lines, bus ducts, welding machine cables
• Medium/small current scenarios:
▪Multi-core cables can be used (less affected by skin effect)
▪Typical applications: Household appliance power cords, control signal wires

▷ Mechanical Movement Requirements
| Movement Type | Recommended Cable | Reason |
| Fixed installation | Single-core cable | High tensile strength, less deformation |
| Occasional movement | Multi-core flexible cable | Moderate flexibility with durability |
| Frequent bending/drag chain movement | Special multi-core drag chain cable | Bending endurance >1 million cycles |

▷ Installation Environment Conditions
• Wiring in confined spaces:
▪Multi-core cables (good flexibility, small bending radius)
▪Examples: Automotive wiring harnesses, cabinet internal wiring
• Outdoor/underground installation:
▪Armored single-core cables (resistant to mechanical damage)
▪Examples: YJV22 underground cables
▷ Signal Transmission Requirements
• High-frequency signals (>1MHz):
▪Shielded multi-core cables (twisted-pair structure for interference resistance)
▪Examples: USB3.0 cables, Ethernet cables
• Power frequency (50/60Hz):
▪Single-core cables are more economical
▪Examples: Household BV wiring

▷ Cost-Benefit Analysis
• Advantages of single-core cables:
▪Material cost about 20-30% lower
▪Higher installation labor cost (need to consider bending radius)
• Advantages of single-core cables:
▪Save over 30% installation time
▪Lower long-term maintenance costs
▷ Safety and Compliance Requirements
• Fire protection standards:
▪Concealed wiring in buildings requires flame-retardant type (e.g., WDZ-BYJ)
▪Low-smoke zero-halogen cables for subways/tunnels
• Industry standards:
▪Power systems follow GB/T 12706
▪Automotive wiring harnesses comply with ISO 6722
Special Scenario Handling Suggestions
• Vibration environments:
▪Multi-core cables need anti-vibration connectors
▪Single-core cables should use clamps for fixation
• High-temperature workshops:
▪Choose silicone rubber insulated multi-core cables (-60℃~200℃)
▪Or mineral insulated single-core cables
• Corrosive environments:
▪Use fluoroplastic outer sheath
▪Armored cables + anti-corrosion coating
○ By systematically evaluating these key factors, cable selection can meet both technical requirements and economic benefits. It is recommended to combine specific working condition parameters in actual projects and refer to IEC or GB standards for final confirmation.
▶ Precautions
When actually using multi-core and single-core cables, the following key points require special attention to ensure safe and reliable operation:
▷ Installation Precautions
• Key Points for Multi-core Cable Installation
▪Bending radius ≥6 times cable diameter to prevent internal conductor breakage
▪Must use dedicated crimp terminals to avoid strand separation causing poor contact
▪Reserve 20% extra length in drag chain applications
▪Direct wrapping with electrical tape at connection points is prohibited
• Key Points for Multi-core Cable Installation
▪Minimum bending radius ≥10 times cable diameter (e.g. 60mm radius for 6mm² cable)
▪Fixing interval ≤1.5m (to prevent sagging due to self-weight)
▪Cross-sectional area should not exceed 40% of pipe diameter when conduiting
▪Terminals require stress relief treatment (e.g. using cable lugs)
▷ Environmental Adaptation
| Environmental Factor | Multi-core Solution | Single-core Solution |
| Humid environment | Waterproof type (e.g. JHS) | Moisture-proof (e.g. VV22) |
| High temperature | Silicone rubber (200℃) | Mineral insulated (250℃) |
| Corrosive environment | Polyurethane sheath | Tinned copper+fluoroplastic |

▷ Safety Protection Measures
• Multi-core cables:
▪Install spring protective sleeves for mobile use
▪Ensure proper shielding layer grounding for signal cables
▪Avoid prolonged contact with oils
• Single-core cables:
▪Consider eddy current loss for large cross-sections (≥50mm²)
▪Use triangular arrangement for three-phase systems
▪Metal armor layer must be reliably grounded
▷ Maintenance Requirements
• Routine Inspection Focus
▪Multi-core: Check for jacket wear and broken strands
▪Single-core: Check insulation aging and connection point overheating
• Testing Frequency
▪Fixed lines: Annual insulation resistance test
▪Mobile lines: Quarterly comprehensive inspection
▪Critical parts: Monthly infrared thermography inspection
▷ Common Issue Handling
• Multi-core cable faults:
▪Symptom: Significant signal interference
▪Solution: Check shield grounding, install ferrite core
• Single-core cable faults:
▪Symptom: Overheating at joints
▪Solution: Re-crimp and apply conductive paste
▷ Special Application Warnings
▪Medical equipment: Must use medical-grade cables (e.g. IEC 60601 compliant)
▪Explosive environments: Use intrinsically safe cables
▪PV systems: DC side requires special PV cables
▼ Appendix: Cable Life Reference ▼
| Cable Type | Fixed Install | Mobile Use | Harsh Env. |
| Multi-core | 15-20 years | 3-5 years | 1-3 years |
| Single-core | 25-30 years | N/A | 5-8 years |
▼ Important Notes ▼
✅ Strictly prohibit mixing different conductor materials (e.g. direct copper-aluminum connection)
✅ Cable capacity must be recalculated for line modifications
✅ Replace cables that exceed service life even if appearance is intact
○ By strictly adhering to these precautions, circuit safety can be maximized and service life extended. It is recommended to establish a complete cable management file to record key information such as installation dates and test data.
No comments to show.


Leave a Comment