Glossary of Wiring Harness Industry Jargon

Table of contents
Types and Architecture of Wiring Harnesses
In automotive, industrial equipment, and emerging technology fields, wiring harnesses act as the “neural blood vessels,” responsible for power transmission and signal control. Below, we dissect the jargon of wiring harness types and architectures through technical parameters, application scenarios, and industry trends:
1. High Voltage Harness
• Definition: Designed for new energy vehicles, transmitting over 300V high-voltage electricity to connect components like battery packs, motors, charging ports, and DC/DC converters.
• Technical Core:
▪Voltage Resistance: Typically 600V/1000V (higher for specific models);
▪Shielding Design: Dual-layer shielding with aluminum foil + braided mesh to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI);
▪Material Selection: Silicone/cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulation layer with a temperature range of -40℃ to 200℃.
• Industry Challenges: Costs account for over 50% of total vehicle wiring harness expenses, with only 30% localized production (e.g., TE Connectivity and Aptiv dominate the high-end market).
• Jargon Extensions:
▪“Three-Power Bodyguard”: Engineers’ nickname for high-voltage harnesses due to their critical role in battery, motor, and electronic control safety;
▪“Orange Alert”: High-voltage harnesses often use bright orange sheathing to warn maintenance personnel of electrical hazards.

2. Low Voltage Harness
• Definition: Mainstream harness for traditional fuel vehicles and low-voltage electronic systems, transmitting 12V/24V power to connect devices like lights, dashboards, and air conditioners.
• Technical Features:
▪Standardized Wire Gauges: 0.5mm²~6.0mm², categorized by current load;
▪PVC Dominance: 80% of harnesses use PVC insulation (low cost but limited to 105℃);
▪Universal Connectors: German automakers prefer TE Connectivity’s AMP series, while Japanese brands use Yazaki standards.
• Industry Status:
▪Red Ocean Market: Unit prices are less than 1/5 of high-voltage harnesses, with gross margins below 15%;
▪“Ant Migration”: Industry joke about the low-margin, high-volume business model.

3. Flat Flexible Harness
• Definition: Flat harnesses using FPC (flexible printed circuits) or parallel wire layouts to enable automated production.
• Technical Breakthroughs:
▪Space Efficiency: Thickness reduced to 1/3 of traditional harnesses; Tesla Cybertruck cut total length by 77%;
▪Topology Optimization: “Tree-like branching” design minimizes nodes (e.g., CelLink’s patented topology).
• Applications:
▪Robot Joints: Withstands over 10 million bends (e.g., KUKA robotic arm harnesses);
▪Wearable Devices: Medical sensor harnesses that flex with body movements.
• Jargon:
▪“2D Revolution”: Refers to the shift from 3D to 2D flat harness designs;
▪“Harness LEGO”: Modular plug-and-play design for easy replacement and repair.

4. Modular Harness
• Definition: Harnesses split into standardized functional modules for rapid assembly via plug-and-play interfaces (e.g., HSD/MQB).
• Technical Advantages:
▪Reduce cost and increase efficiency: the design cycle is shortened by 30%, and the production line switching efficiency is increased by 50%;
▪Fault Isolation: Failed modules can be replaced individually, avoiding full harness scrapping.
• Case Studies:
▪Volkswagen MEB Platform: Modules divided by functional domains (powertrain, cabin, etc.);
▪NIO Battery Swap System: Modular battery harnesses enable 3-minute swaps.
• Industry Trend:
▪“Software-Defined Harness”: OTA updates adjust functional allocation (e.g., IM L7’s ICC domain control).

5. Special Harness
• Definition: Custom harnesses for extreme environments or specialized applications, exceeding automotive-grade technical requirements.
• Subcategories:
▪Radiation-Resistant Harnesses: For spacecraft (e.g., NASA Mars rover harnesses), withstand 100kGy radiation;
▪Deep-Sea Harnesses: Pressure resistance over 100MPa for subsea exploration (e.g., Jiaolong submersible);
▪Cryogenic Superconducting Harnesses: Niobium-titanium alloy wires operating at -269℃ (e.g., MRI machines).
• Jargon:
▪“Dancing on a Knife’s Edge”: Describes extreme reliability requirements;
▪“Golden Blood Vessels”: Refers to ultra-expensive harnesses (e.g., aircraft engine harnesses) costing over ¥10,000 per meter.

6. Architecture Evolution Trends
• Domain Control Architecture:
▪Reduces ECUs from 100+ to 5-7 domain controllers, shifting from distributed to centralized systems (e.g., Tesla Model 3);
▪Total harness length decreases by 20%~40%, but high-speed data lines increase (e.g., Ethernet replacing CAN bus).
• Wireless Alternatives:
▪Huawei’s “SparkLink” enables wireless battery module communication, cutting BMS harnesses by 50%;
▪Tesla’s “Vehicle Wireless Power System” patent explores integrating wireless charging and signal transmission.

Appendix: Industry Data Comparison
| Harness Type | Unit Price (CNY/set) | Annual Growth Rate | Localization Rate | Key Technical Barriers |
| High Voltage Harness | 2500-4000 | 35% | 30% | Silicone Extrusion Technology |
| Flexible Harness | 800-1500 | 50% | 10% | Laser-Cut FPC |
| Aerospace Special Harness | 100k+ | 8% | 5% | Aerospace Material Certification |
Conclusion: From “copper-core rubber wires” to “smart harness matrices,” wiring harness architectures are undergoing disruptive transformation. Mastering this jargon is not just a technical passport but a key to deciphering industry trends.

Production Processes & Materials
The essence of wiring harness production lies in “materials define performance, processes define efficiency.” From copper wires to finished harnesses, the process involves dozens of steps and hundreds of materials. Below are the industry’s “hardcore terms” and hidden rules:
1. Cutting/Crimping/Pre-Assembly/Final Assembly (Four Core Processes)
• Definition: The four core manufacturing processes, accounting for over 60% of costs, with 70% reliance on manual labor.
• Technical Details:
▪Cutting & Stripping:
- Laser Stripping: ±0.1mm precision, replacing blades to avoid copper damage (Tesla patented);
- Wire Sorting: Classified by color and gauge to prevent “mixed wires” (using mismatched specifications).
▪Crimping:
- Hexagonal Crimping: Tightens terminal-wire bonds, reducing resistance by 15% (e.g., TE Connectivity);
- Pressure Monitoring: Real-time force detection (50N~200N), boosting yield to 99.9%.
▪Pre-Assembly:
- Error-Proof Fixtures: Color/shape-coded to avoid connector misalignment (e.g., Volkswagen MQB standards);
- Tape Wrapping: Overlap method with ≤2mm tension error.
▪Final Assembly:
- Template Wiring: Branches fixed per 1:1 drawings, relying on veteran “hand feel” (called “embroidery work”);
- Air Tightness Test: 5 Bar pressure post-glue injection for waterproofing (mandatory for EVs).
• Industry Pain Points:
▪“Human Wave Tactics”: Only 8–10 sets/day per worker; automation rate <30%;
▪“Crimping Mysticism”: Hidden defects like oxidation/burrs cause >5% OEM claims.

2. Dual Wall Heat Shrink
• Definition: Dual-layer heat-shrink tubing (inner hot-melt adhesive + outer polyolefin), replacing traditional electrical tape.
• Technical Specs:
▪Shrink Ratio: 3:1 or 4:1 for varied wire gauges;
▪Temperature Resistance: -55℃~175℃ (silicone up to 200℃);
▪Flame Rating: UL VW-1 (vertical burn test).
• Applications:
▪High-Voltage Sealing: IP67/IP69K waterproofing for battery connectors;
▪Abrasion Resistance: Protects chassis harnesses from stone impacts.
• Jargon:
▪“Heat Shrink Lord”: Engineers’ nickname for its “magic activation by heat”;
▪“Tape Killer”: Trend of replacing PVC tape with dual-wall tubing.

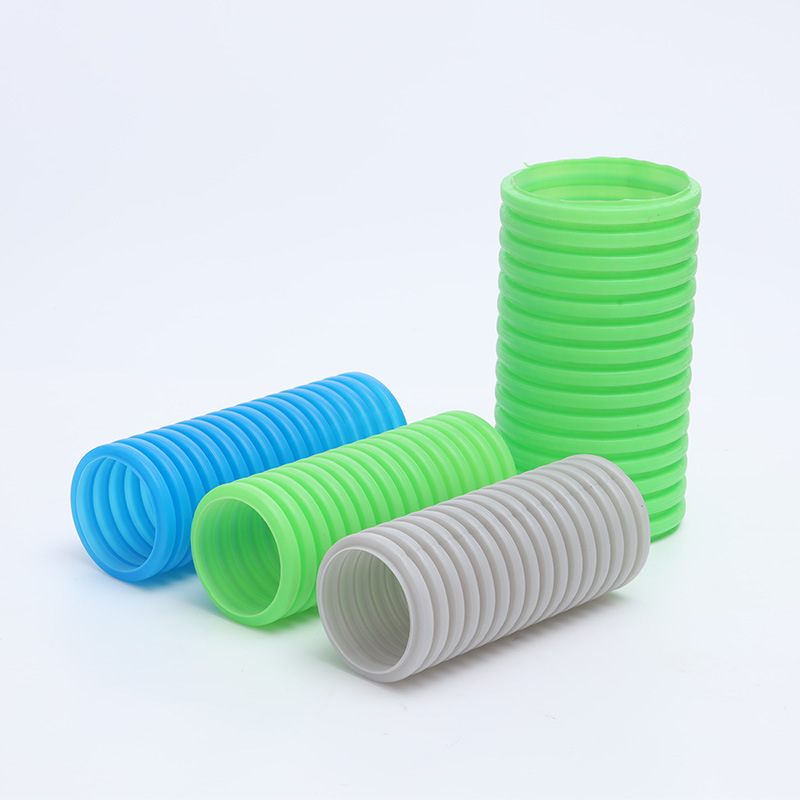
3. Corrugated Conduit
• Material Showdown:
▪PP Conduit: -40℃ low-temp resistance, 100k bend cycles (for northern climates);
▪PA Conduit: V0 flame retardant, 150℃ temperature-resistant (preferred for EVs).
• Industry Secrets:
▪“Color Code”: Black for UV resistance, blue for oil resistance (construction machinery);
▪“Price Gap”: Domestic conduits are 40% cheaper but 20℃ less temperature-resistant.
• Failure Case:
▪“Conduit Gate”: A brand recalled harnesses due to PA conduit brittleness in cold (loss >¥200M).

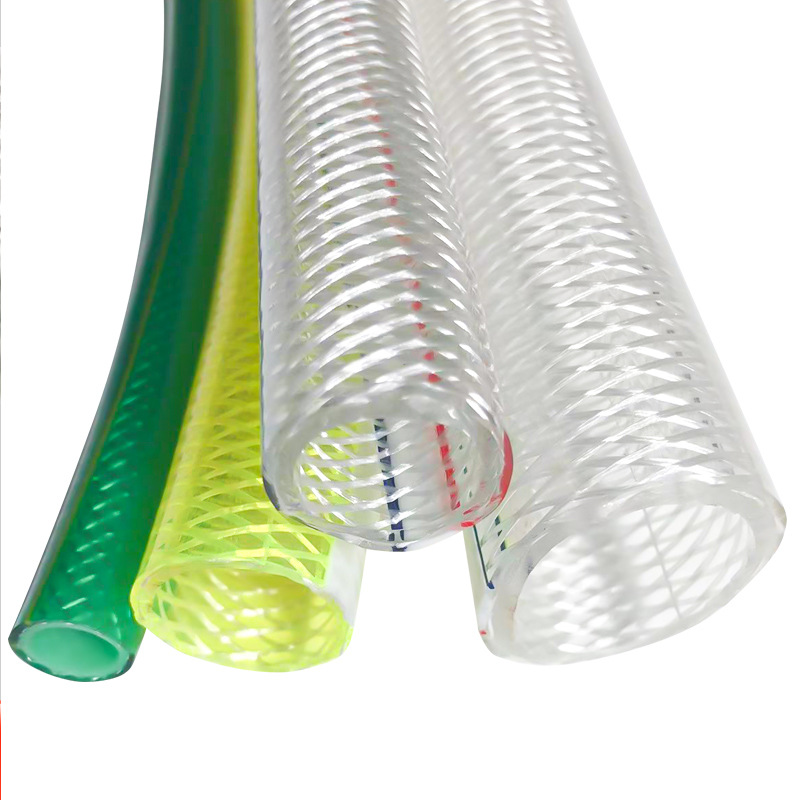
4. Flexible Conduit
• Structural Secrets:
▪Stainless Steel Braided: 500℃ high-temperature resistant for engine bays (¥30/m);
▪Nylon Spiral: 50% lighter for door harnesses (favored by Japanese OEMs).
• Production Pitfalls:
▪“Cutting Hand Effect”: Unpolished edges injure workers (15% Work-related injury rate increase);
▪“Stretch Curse”: Low-quality conduits fail to retract, causing harness looseness.
• Jargon:
▪“Transformers”: Adaptability to complex routing;
▪“Metal Blood Vessels”: Nickname for stainless steel conduits in high-heat zones.

5. Hard Gold/Soft Gold Plating
• Technical Differences:
▪Hard Gold:
- Containing cobalt/nickel alloy, thickness of 0.5~1.27μm, wear-resistant 5000 times of insertion and removal (such as Type-C interface).
- 30% cheaper than soft gold but poor solderability (requires laser assist).
• Soft Gold:
▪Purity 99.99%, thickness 0.05~0.1μm, used for chip bonding (Wire Bonding);
▪Prone to oxidation, stored in nitrogen cabinets (called “golden cage”).
• Industry Taboos:
▪“Black Pad Crisis”: Incomplete pre-plating causes nickel oxidation (solder failure);
▪“Gold finger killer”: hard gold thickness is less than 0.3μm, plugging and unplugging 100 times that exposed copper.
6. Material Innovation Trends
• Eco-Friendly Alternatives:
▪Halogen-free fuel retardant: mandatory under the EU ELV Directive, temperature resistance upgraded to 125°C (e.g. BASF Ultramid®);
▪TPU Replacing PVC: 50% recyclability boost, 3x oil resistance (Tesla Cybertruck).
• Lightweight Tech:
▪Aluminum Wires: 60% lighter than copper, requiring special crimping (e.g., Audi Q6 e-tron);
▪Carbon Fiber Shielding: Replaces metal braiding, cuts weight by 70% (aerospace tech).

Appendix: Industry Data Comparison
| Material | Temperature Resistance | Cost (CNY/m) | Eco-Friendliness | Applications |
| PVC Insulation | -40℃~105℃ | 0.8~1.2 | Halogenated | Low-Voltage Harnesses |
| XLPE Insulation | -50℃~150℃ | 3.5~5.0 | Halogen-Free | High-Voltage Harnesses |
| Silicone Sheath | -60℃~200℃ | 12.0~18.0 | Biodegradable | Charging Gun Harnesses |
| PA66 Corrugated Conduit | -40℃~170℃ | 6.0~8.0 | Hard to Recycle | Engine Harnesses |
Conclusion: From “manual assembly” to “machine vision,” from “tape-bound” to “heat-shrink armor,” the evolution of harness production is a saga of balancing cost, efficiency, and reliability. Mastering this jargon lets you decode “material magic” in supplier talks and unravel “process puzzles” on the factory floor.
Inspection & Quality Control
As the “neural blood vessels” of vehicles, wiring harness reliability directly impacts safety. From micron-level terminal crimping to kilometer-long assemblies, inspection and quality control are the industry’s “lifelines.” Below are the covert terms, hidden rules, and infamous failure cases:
1. AI Vision Inspection
• Technical Principles:
▪High-resolution cameras (5μm precision) capture connector states, with AI algorithms detecting defects like tilted terminals, missing pins, or cracked housings.
▪Deep Learning Model: Trained on 1M+ defect samples, achieving 99.99% accuracy (e.g., Hikvision solutions).
• Industry Advantages:
▪Replaces Manual Checks: AI processes 50x faster than human inspectors (2000 terminals/day per person);
▪Data Traceability: Defect images linked to production batches for instant root-cause analysis.
• Jargon:
▪“AI Judge”: Mocks the system’s ruthlessness in flagging even 0.1mm misalignments;
▪“Pixel Hunter”: Engineers’ frustration while tweaking image contrast for algorithm optimization.

2. Test Coupon (Impedance Strip)
• Definition: Miniature test strips embedded in PCBs to validate impedance consistency (e.g., USB 3.2 requires 90Ω±10%).
• Design Secrets:
▪“Sandwich Structure”: Reference layer spacing error must <5%, or impedance fluctuates >20%;
▪Probe Traps: Test point diameter ≥0.5mm to prevent probe slippage (called “needle tip dancing”).

3. Black Pad
• Formation Mechanism: Nickel layer oxidation during PCB immersion gold plating creates nickel sulfide (Ni₃S₂), causing weak or detached solder joints.
• Detection Challenges:
▪Invisible Killer: No visible defects; requires SEM+EDS analysis (¥500/point);
▪“Random Curse”: 0.01% occurrence rate with no full interception (e.g., autonomous chip batch rework).
• Jargon:
▪“Black Pad Assassin”: Highlights its stealth and destructiveness;
▪“Gilded Surface”: Mocks the pristine exterior hiding internal black pads.
4. Gold Finger
• Plating Standards:
▪Hard Gold: Thickness 0.3~1.27μm, wear-resistant plugging and unplugging ≥5000 times (such as memory strip interface);
▪Soft Gold: 0.05~0.1μm thick for wire bonding, 99.99% purity.
• Critical Defects:
▪“Gold Brittleness”: Over-thick plating causes brittle fractures
▪“Gold Creep”: Contaminated plating solution spreads gold to non-contact areas (80% short-circuit risk).
• Jargon:
▪“Bling Gold”: Mocks excessive plating (costly yet performance-neutral);
▪“Gold Finger Killer”: Refers to the tester who wears the coating due to frequent plugging and unplugging.
5. High-Voltage Harness “Three Deadly Tests”
• Three Tortures:
▪Withstand Voltage Test: 2x rated voltage (e.g., 2000V for 1000V harness), leakage current <10mA;
▪Insulation Resistance: 500V megger test, resistance >100MΩ (>10MΩ in humidity);
▪Partial Discharge: Measures PDIV (Partial Discharge Inception Voltage), ≥1.2kV for EVs.
• Industry Pain Points:
▪“Ghost Discharge”: Silicone harness bubbles cause undetectable partial discharges;
▪“Test Fatigue”: High-voltage equipment costs >¥2M, pushing SMEs to cut corners.

6. Failure Analysis “Four Guardians”
• X-Ray (CT Scan):
▪Inspects terminal crimping voids (<10% allowed), 1μm precision;
▪“Black & White Movie”: Engineers’ nickname for X-ray images.
• Cross-Section Analysis:
▪Polished epoxy samples observed under microscopes for ≥80% crimp deformation;
▪“Dissection Master”: Senior technicians specializing in cross-sections.
• Infrared Thermal Imaging:
▪Locates weak joints via temperature rise (>5℃ difference fails);
▪“Temperature Hunter”: Title for those spotting hidden hotspots.
• Salt Spray Test:
▪5% NaCl spray for 96 hours to check for corrosion (e.g., VW TL226);
▪“Salted Fish Test”: Mocks harnesses’ ordeal in salt chambers.
Appendix: Inspection Standard Comparison
| Inspection Item | International Standard | OEM Stringent Version | Common Cheating Tactics |
| Terminal Crimping Force | USCAR-21 | Volkswagen VW60330 | Lowering pressure sensor thresholds |
| Waterproof Rating | IP67 | Tesla IP69K | Testing only partial connectors |
| Bend Cycle Lifetime | 500k cycles | BMW 1M cycles | Reducing test bending angles |
Conclusion: From the “AI Judge” to the “Three Deadly Tests,” from the “Gold Finger Killer” to the “Four Guardians,” the world of harness inspection blends technological rigor with human-machine cunning. Mastering this jargon empowers you to see through suppliers’ tricks and dominate the battlefield of quality.
Geen reacties om te tonen.


Laat een reactie achter