Explanation of Normal and Dangerous Temperature of Wiring Harness Getting Hot
Is it normal for a wire harness to get hot? The key to look at the temperature! Slight heating is a normal phenomenon of current transmission, but abnormally high temperatures are a hidden crisis. Overload, poor contact or aging may lead to wire harness temperature soaring, which may affect the life of the equipment, or cause fire accidents.
Wiring harnesses made of different materials have different temperature resistance: ordinary PVC wire 70 ℃ on the danger, and silicone wire can withstand high temperatures of 200 ℃. Automotive wiring harnesses should usually be able to withstand 105 ° C, and household wires should not exceed 50 ° C ambient temperature.
How to judge? Hand-measured 60 ℃ is the safety threshold, more than that need to be vigilant. Professional testing suggests the use of infrared thermometer, accurate and safe. Prevention is better than cure: Proper wiring, regular checking and load matching make your electricity safer!

Table of contents
- Explanation of Normal and Dangerous Temperature of Wiring Harness Getting Hot
- I. Is It Normal for Wiring Harness to Heat Up?
- 1. Normal Heating Conditions
- (1) Heat Generation Due to Current Flow Through Conductors
- (2) Short-Term High-Load Operation
- (3) Environmental Temperature Effects
- 2. Abnormal Heating Conditions
- (1) Overload (Current Exceeds Wiring Harness Capacity)
- (2) Poor Contact (High Contact Resistance)
- (3) Short Circuit or Insulation Damage
- (4) Poor Heat Dissipation
- 3. How to Initially Determine If Heating Is Normal?
- ▶ Conclusion:
- Ⅱ. Hazardous Temperature Standards
- Ⅲ. Response Measures
- 1. Slight Heating (≤60°C)
- Possible causes: Normal current flow, high ambient temperature.
- Response measures:
- 2. Noticeable Heating (60~90°C)
- Possible causes: Slight overload, poor contact, or inadequate heat dissipation.
- Response measures:
- 3. High-Temperature Hazard (90~120°C)
- Possible causes: Severe overload, short circuit, or insulation aging.
- Response measures:
- 4. Extreme High Temperature (>120°C)
- Risk level: Extremely high, potential fire hazard.
- Emergency steps:
- 5. Long-Term Preventive Measures
- ▶ Summary
- I. Is It Normal for Wiring Harness to Heat Up?
I. Is It Normal for Wiring Harness to Heat Up?
It is common for wiring harnesses to heat up during operation, but excessively high temperatures may indicate potential safety hazards. Determining whether the heating is normal requires a comprehensive analysis of the degree of heating, duration, environmental factors, and accompanying phenomena.
1. Normal Heating Conditions
(1) Heat Generation Due to Current Flow Through Conductors
• According to Joule’s Law (Q=I²Rt), when current flows through a conductor, heat is naturally generated due to resistance, and a slight temperature rise (e.g., 10-20°C) is normal.
• Example: After prolonged use of household appliances, the power cord may feel slightly warm to the touch without any unusual odor, which is generally harmless.
(2) Short-Term High-Load Operation
• Certain devices (e.g., motor startups, high-power appliances) experience a surge in current for a short period, causing temporary heating of the wiring harness, but the temperature returns to normal once the load decreases.
• Example: During car startup, the starter motor wiring harness heats up briefly but cools down after the engine starts.
(3) Environmental Temperature Effects
• High-temperature environments (e.g., engine compartments, industrial equipment interiors) can exacerbate the temperature rise of wiring harnesses, but as long as it remains within the material’s heat resistance range, it is still normal.
• Example: Wiring harnesses in a car engine compartment may reach 60-80°C in summer, but if high-temperature-resistant materials (e.g., silicone insulation) are used, they can still operate safely.

2. Abnormal Heating Conditions
(1) Overload (Current Exceeds Wiring Harness Capacity)
• An undersized wire gauge or excessive load can cause the current to exceed safe limits, leading to sustained high temperatures (>60°C) in the wiring harness.
• Warning signs: Softening, deformation, or even melting of the wire insulation.
(2) Poor Contact (High Contact Resistance)
• Oxidation, looseness, or corrosion of connectors can increase contact resistance, causing localized overheating (potentially exceeding 100°C).
• Warning signs: Burnt or blackened connectors accompanied by a scorched smell.

(3) Short Circuit or Insulation Damage
• Damaged insulation in the wiring harness can cause a short circuit, leading to a sudden surge in current that rapidly heats up or even burns out the harness.
• Warning signs: Smoke, sparks, or blown fuses.
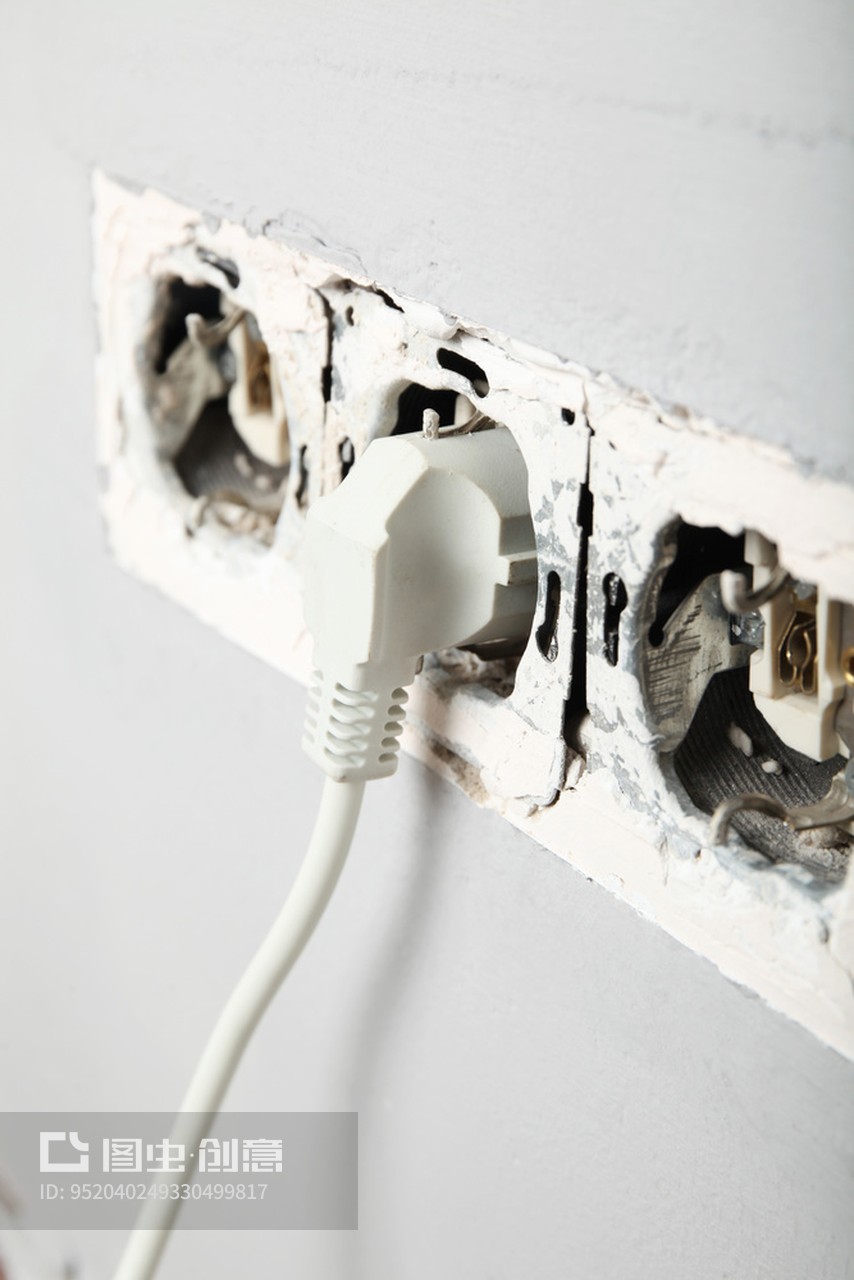

(4) Poor Heat Dissipation
• Tight bundling, enclosed spaces, or proximity to high-temperature components can trap heat, causing the temperature to rise continuously.
• Warning signs: The entire wiring harness feels scalding hot and does not cool down over time.
3. How to Initially Determine If Heating Is Normal?
| Feature | Normal Heating | Abnormal Heating |
| Temperature Range | ≤ Ambient temp + 30°C (touchable) | ≥60°C (scalding, cannot touch for long) |
| Duration | Short-term, cools after load reduction | Sustained high temperature, no cooling |
| Wiring Condition | No deformation or unusual odor | Insulation softens, turns black, or smokes |
| Accompanying Signs | No circuit abnormalities | Device malfunctions, tripping, or blown fuses |
▶ Conclusion:
• If the wiring harness is only slightly warm with no other abnormalities, it is usually normal.
• If the temperature is excessively high (scalding), accompanied by a burnt smell or damaged insulation, power must be cut off immediately to inspect and prevent fire hazards.
Ⅱ. Hazardous Temperature Standards
Whether the temperature of a wiring harness is dangerous depends on its insulation material, operating environment, and load conditions. Below are the temperature resistance standards for different insulation materials and corresponding safety thresholds for reference:
1. Hazardous Temperature Standards by Insulation Material
| Insulation Material Type | Long-term Withstand Temp (°C) | Short-term Peak Temp (°C) | Overheating Risks | Typical Applications |
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | 70~90 | 105 | Softening, deformation, toxic gas release | Household appliances, low-voltage wiring harnesses |
| XLPE (Cross-linked Polyethylene) | 90~105 | 125 | Insulation cracking, electrical performance degradation | Automotive wiring harnesses, industrial cables |
| Silicone Rubber | 150~180 | 200 | Reduced elasticity, accelerated aging | High-temperature environments (e.g., engine compartments) |
| PTFE (Teflon) | 200~260 | 300 | Stable under extreme heat but costly | Aerospace, military equipment |
| EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber) | 90~125 | 150 | Hardening, cracking | High-voltage wiring harnesses for new energy vehicles |



2. Hazardous Temperature Thresholds by Safety Level
| Temperature Range (°C) | Risk Level | Potential Impacts | Recommended Actions |
| <60 | Safe | Normal temperature rise, no risk | No special measures needed |
| 60~90 | Warning | Hot to touch, may accelerate aging over time | Check load and heat dissipation |
| 90~120 | Hazardous | Insulation may soften or deform | Immediately investigate overload or poor contact |
| 120~150 | High Risk | High probability of insulation failure or short circuit | Shut down for inspection, replace with high-temp resistant wires |
| >150 | Critical | May cause fire | Cut power and seek professional repair |
3. Temperature Limits for Wiring Harnesses in Different Applications (Reference Standards)
| Application Scenario | Maximum Allowed Temp Rise (°C) | Industry Standard | Notes |
| Household Appliances | ≤50 (Ambient +50) | IEC 60335 | Avoid plastic component deformation |
| Automotive Low-Voltage Wiring | ≤105 (Short-term 125) | ISO 6722 | Engine compartments require high-temp resistance |
| New Energy Vehicle High-Voltage Wiring | ≤125 (Short-term 150) | LV 112-3 | Special materials needed for high current |
| Industrial Equipment Cables | ≤90 (Standard) | UL 758 | Mechanical strength must be considered |
▶ Key Conclusions
• Safety Threshold: For ordinary wiring harnesses, sustained temperatures >60°C require attention, while >90°C necessitates immediate inspection.
• Material Determines Limits: Silicone/Teflon wires can withstand higher temperatures but at higher costs.
• Industry Variations: Temperature resistance standards differ for automotive, household, and industrial wiring harnesses—must match application scenarios.
▷ It is recommended to use an infrared thermometer for regular monitoring to ensure wiring harnesses operate within safe limits.
Ⅲ. Response Measures
When discovering that a wiring harness is heating up, appropriate measures should be taken based on the temperature level to avoid insulation aging, short circuits, or even fire hazards. Below are response methods and preventive recommendations for different temperature ranges:
1. Slight Heating (≤60°C)
Possible causes: Normal current flow, high ambient temperature.
Response measures:
• Monitor whether the heating persists; if it doesn’t worsen, continued use is acceptable.
• Ensure proper ventilation around the wiring harness and avoid accumulation in enclosed spaces.
• Regularly inspect the harness’s appearance for signs of aging or damage.
2. Noticeable Heating (60~90°C)
Possible causes: Slight overload, poor contact, or inadequate heat dissipation.
Response measures:
| Inspection Item | Specific Actions | Notes |
| Load Matching | Verify if current exceeds the harness’s rated capacity | Refer to wire gauge specifications (e.g., 1mm² copper wire ≈ 10A) |
| Contact Point Check | Inspect terminals and connectors for oxidation or looseness | Measure contact resistance with a multimeter (should be <0.5Ω) |
| Heat Dissipation Optimization | Avoid tight bundling or proximity to heat sources | Install heat-resistant sleeves in high-temperature areas |
3. High-Temperature Hazard (90~120°C)
Possible causes: Severe overload, short circuit, or insulation aging.
Response measures:
• Immediately reduce the load: Disconnect some devices or suspend usage.
• Check for short circuits: Inspect the harness for damage or grounding issues.
• Replace wiring: If the wire gauge is insufficient or insulation is degraded, switch to high-temperature-resistant wires (e.g., silicone-insulated wires).
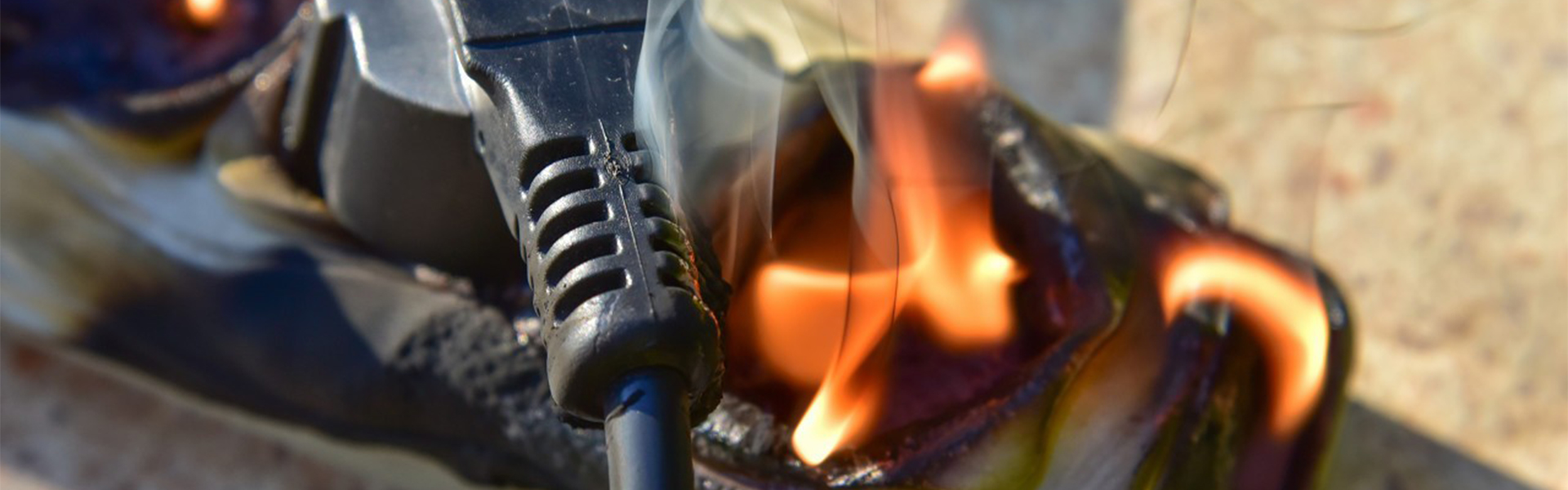
4. Extreme High Temperature (>120°C)
Risk level: Extremely high, potential fire hazard.
Emergency steps:
• Cut off power: Prioritize disconnecting the power supply to prevent further damage.
• Check for burn marks: Look for melted insulation or carbonized spots.
• Professional repair: Replace the entire damaged section of the harness; avoid temporary fixes like taping.

5. Long-Term Preventive Measures
| Measure | Implementation Method | Effect |
| Proper Wiring Layout | Avoid contact with high-temperature components (e.g., exhaust pipes, engines) | Reduces environmental heat impact |
| Appropriate Wire Gauge Selection | Choose wire cross-sectional area based on current (e.g., use ≥2.5mm² for high current) | Lowers resistance-induced heating |
| Regular Maintenance | Annual inspection of insulation and terminal corrosion | Identifies potential issues early |
| Use of High-Temperature Materials | Employ silicone/Teflon-insulated wires in high-temperature areas | Enhances heat resistance |
▶ Summary
• Slight heating: Enhance monitoring and improve heat dissipation.
• Noticeable heating: Investigate load, contact resistance, and heat dissipation issues.
• High-temperature hazard: Immediately stop use and conduct repairs; replace the harness if necessary.
• Prevention is key: Proper selection, standardized wiring, and regular maintenance are crucial.
▷ By implementing tiered responses, the risk of wiring harness overheating can be effectively reduced, ensuring electrical safety.

表示できるコメントはありません。


コメントする